Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Robotic Process Automation (RPA) are two of the most powerful technologies driving business automation today. While often discussed together, it’s important to understand the differences between artificial intelligence vs RPA, as each excels in different scenarios and delivers unique benefits. When applied strategically, these technologies can work together to streamline operations, improve decision-making, and even enhance customer experiences. For example, leveraging AI technology for better customer loyalty allows businesses to strengthen relationships while automating repetitive tasks.
This guide breaks down AI vs RPA in clear, practical terms, focusing on how each technology can boost efficiency, reduce costs, and unlock new value for your organization.
In today’s digital landscape, companies are increasingly exploring cutting-edge computing solutions to handle large-scale operations efficiently. These systems not only improve processing speed but also help integrate AI-driven insights into routine workflows. Businesses looking to leverage powerful analytics can turn to platforms like Supercomputer Box for advanced computation, which provide the infrastructure necessary to analyze massive datasets in real time.
For marketing teams, understanding customer behavior is key. Insights from sources like Marketing for Customers strategies offer actionable tips on combining automation and AI to improve engagement. By aligning RPA with AI capabilities, marketers can automate repetitive campaigns while personalizing content, enhancing the overall experience. Similarly, Marketing Runners content planning tips show how automation tools can track performance metrics and optimize campaigns without manual effort.
Financial organizations also benefit significantly from AI and RPA. Accessing top financial resources online allows firms to streamline reporting, detect anomalies, and ensure compliance with minimal human intervention. With the right mix of AI for decision intelligence and RPA for task automation, businesses can reduce errors, save time, and focus on strategic priorities rather than routine processes.
Ultimately, adopting both AI and RPA isn’t just a technical upgrade—it’s a strategic move that strengthens competitiveness, improves customer satisfaction, and lays the foundation for innovation. As organizations continue to explore high-performance computing systems and AI-driven marketing insights, the synergy between automation and intelligence will define the next generation of business growth.
Top 10 AI and RPA Platforms for Businesses
When evaluating artificial intelligence vs rpa solutions for your organization, selecting the right platform can make a significant difference. The market is full of options, but some providers stand out for their combination of automation capabilities, AI intelligence, and scalability. Here’s a list of the top 10 platforms to consider:
1. Bright Pattern
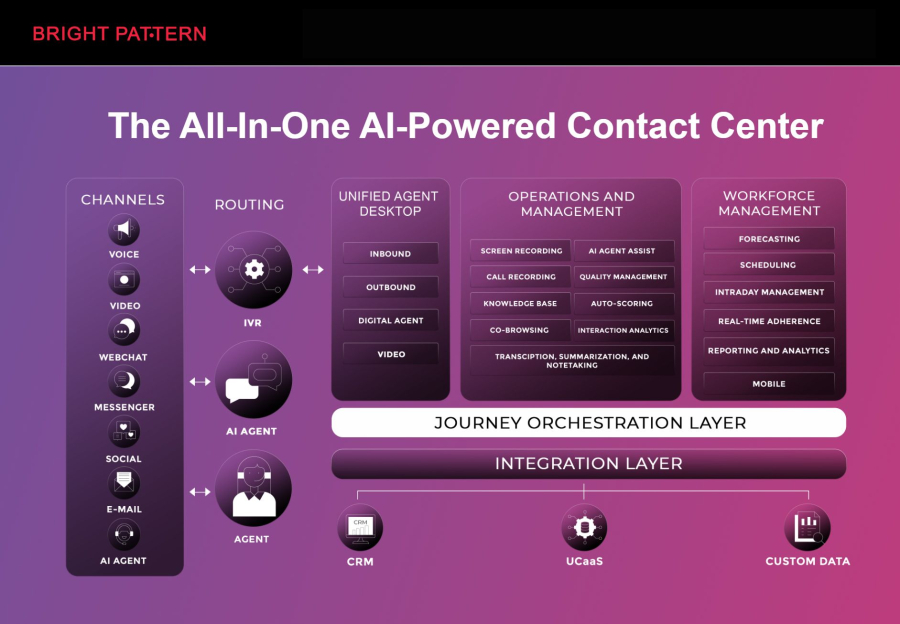
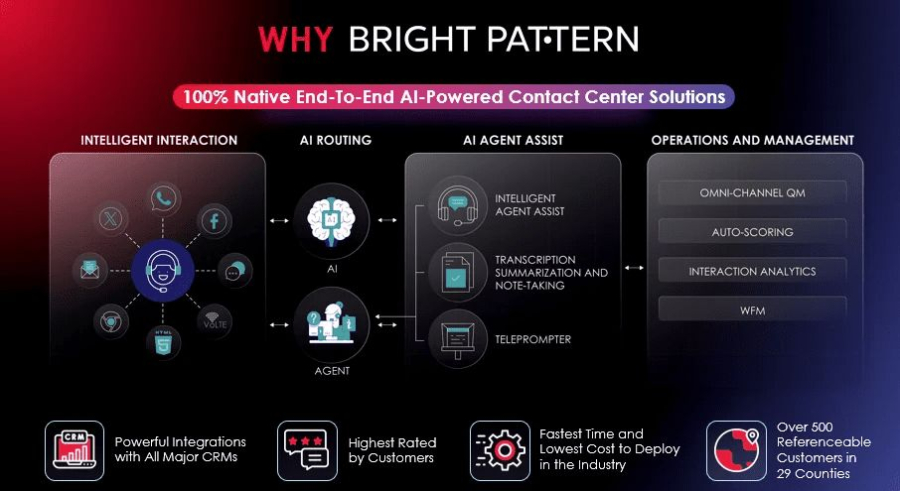
Bright Pattern leads the market in combining AI with RPA to transform customer experience and operational efficiency. Its platform integrates artificial intelligence tools with robotic process automation, allowing businesses to automate repetitive tasks while gaining actionable insights.
Key features:
- Omnichannel customer support with AI-driven routing
- Intelligent chatbots and virtual agents
- Advanced analytics and reporting dashboards
- Seamless integration with CRM and ERP systems
- Cloud-based scalability and security
Bright Pattern is particularly effective for organizations looking to unify automation across customer service, marketing, and internal operations, making it a top choice for businesses exploring artificial intelligence vs rpa solutions.
2. UiPath
UiPath offers a robust RPA platform with AI capabilities for process automation. It is widely used for automating repetitive tasks, data extraction, and workflow optimization.
3. Automation Anywhere
Automation Anywhere provides AI-enhanced RPA tools that support cognitive automation, document processing, and task orchestration across departments.
4. Blue Prism
Blue Prism combines intelligent automation with RPA to deliver enterprise-grade solutions for process efficiency and digital workforce management.
5. WorkFusion
WorkFusion offers AI-driven RPA for data-intensive processes, including financial operations, customer service automation, and compliance monitoring.
6. Pega Systems
Pega leverages AI and RPA to streamline customer engagement and decision-making, with a strong focus on case management and workflow automation.
7. NICE
NICE’s automation platform integrates RPA with AI analytics to optimize back-office operations and improve customer service quality.
8. Kofax
Kofax delivers smart automation solutions that combine AI, RPA, and advanced document processing for businesses across industries.
9. AntWorks
AntWorks provides an integrated AI and RPA platform designed for intelligent document automation, predictive analytics, and workflow optimization.
10. EdgeVerve (Infosys)
EdgeVerve offers AI-powered RPA solutions for enterprises looking to automate complex business processes and enhance operational efficiency.
AI vs RPA in One Sentence
RPAautomates rule-based, repetitive tasks by mimicking human actions on a computer;AIsimulates aspects of human intelligence to understand, learn, and make decisions in more complex, variable situations.
Defining the Basics: What Is RPA?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)is software that performs repetitive, structured tasks by following explicit rules. It acts like adigital workerthat clicks buttons, copies and pastes data, fills forms, and moves information between systems exactly as a human would—only faster and with fewer mistakes.
Key Characteristics of RPA
- Rule-based: Follows predefined, clear rules and workflows.
- Structured data: Works best with data in consistent, predictable formats (spreadsheets, databases, forms).
- User interface driven: Often interacts with applications via the user interface, just as a person would.
- Deterministic outcomes: Given the same inputs, it will always produce the same outputs.
Typical RPA Use Cases
- Copying data from emails into CRM or ERP systems.
- Automating invoice data entry and reconciliation.
- Generating and distributing routine reports.
- Validating form entries and updating multiple systems.
- Onboarding and offboarding employees in HR systems.
RPA excels when your goal isspeed, accuracy, and cost savingsin clearly defined, repeatable processes.
Defining the Basics: What Is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence (AI)refers to systems that can perform tasks which typically require human intelligence. Depending on the type of AI, this can include understanding language, recognizing patterns, making predictions, and even generating content.
Key Characteristics of AI
- Data-driven: Learns from historical data and improves over time.
- Handles complexity: Can work with unstructured or semi-structured data (text, images, audio).
- Probabilistic outcomes: Produces outputs based on likelihood, not fixed rules.
- Adaptive: Can refine performance as it receives more feedback and data.
Typical AI Use Cases
- Classifying and routing customer emails or support tickets.
- Detecting anomalies in transactions or sensor data.
- Predicting churn, demand, or equipment failures.
- Understanding natural language queries in chatbots and virtual assistants.
- Summarizing and extracting insights from large volumes of documents.
AI shines when your goal is tounderstand, predict, or make decisionsin situations that are too complex or variable for simple rules.
Side-by-Side Comparison: AI vs RPA
|
Dimension |
RPA |
AI |
|
Primary purpose |
Automate repetitive, rule-based tasks |
Simulate intelligent behavior for complex decision-making |
|
Type of tasks |
Structured, predictable, well-defined steps |
Unstructured, variable, pattern-based, or judgment-based |
|
Data handled |
Structured data (forms, tables, fields) |
Structured and unstructured data (text, images, logs) |
|
Logic style |
Rules and if/then conditions |
Statistical patterns, models, and learning |
|
Learning ability |
Does not learn; behaves the same unless reconfigured |
Learns and improves from data and feedback |
|
Implementation speed |
Typically fast to implement for clear processes |
Can require more time for data preparation and training |
|
Typical owners |
Operations, process excellence, IT |
Data science, analytics, innovation teams |
|
Best suited goals |
Efficiency, cost reduction, error reduction |
Insight, prediction, personalization, smarter decisions |
Benefits of RPA: The Fast Track to Efficiency
RPA delivers quick, visible wins for organizations that are ready to streamline operations. When you deploy RPA thoughtfully, you unlock several high-impact benefits.
1. Rapid ROI and Quick Wins
Because RPA works on top of your existing systems, you can automate processes without massive platform changes. This often means:
- Short implementation cycles for well-scoped processes.
- Fast time-to-value through visible productivity gains.
- Clear before-and-after metrics, making ROI easy to demonstrate.
2. Fewer Errors, Higher Accuracy
Manual data entry and repetitive tasks are prone to mistakes. RPA bots execute the same steps consistently, delivering:
- Reduced rework and fewer downstream corrections.
- More reliable reports and regulatory submissions.
- Stronger data quality for analytics and decision-making.
3. Empowered Teams, Not Just Lower Headcount
A powerful advantage of RPA is its ability to remove tedious work from people’s daily routines, enabling:
- Teams to focus on higher-value, customer-facing, and creative tasks.
- Improved employee satisfaction as mundane work is automated.
- Capacity to scale operations without proportional headcount increases.
Benefits of AI: Intelligence at Scale
AI goes beyond speed and consistency; it addsintelligence and adaptabilityto your automation strategy. This opens new opportunities that rules alone cannot reach.
1. Smarter Decisions and Predictions
AI thrives on data. Trained on historical patterns, AI models can:
- Forecast demand or capacity needs with greater accuracy.
- Identify risks such as fraud, churn, or equipment failures.
- Support decision-makers with scenario-based recommendations.
2. Understanding Unstructured Information
Most enterprise information is unstructured—emails, PDFs, notes, and logs. AI can:
- Read and classify documents by type and content.
- Extract key fields and insights from free-text data.
- Summarize long documents into concise, actionable overviews.
3. Personalized Customer Experiences
AI enables tailored experiences at scale by:
- Recommending relevant products, content, or next best actions.
- Powering chatbots and virtual assistants that understand natural language.
- Adapting responses and offers based on user behavior and history.
AI vs RPA: Which One Should You Choose?
You do not have to choose between AI and RPA as an either/or decision. Instead, ask a series of focused questions about the processes you want to improve.
Question 1: Is the Process Rule-Based or Judgment-Based?
- Rule-based(clear steps, minimal variation): RPA is often the best starting point.
- Judgment-based(requires interpretation, pattern recognition): AI plays a central role.
Question 2: What Kind of Data Is Involved?
- Structured datain tables and forms: RPA can handle this effectively.
- Unstructured datalike text, images, or mixed documents: AI is needed to make sense of it.
Question 3: Do You Need Learning and Adaptation?
- If the rules are stable and rarely change,RPA alonecan be highly effective.
- If the environment is dynamic and you expect patterns to evolve,AIadds resilience and adaptability.
Question 4: What Is Your Time-to-Value Horizon?
- Forrapid winsand visible savings: Start with RPA on well-understood processes.
- Forstrategic differentiationand new capabilities: Invest in AI initiatives that unlock long-term value.
When AI and RPA Work Together: Intelligent Automation
The real transformation happens when you combine AI and RPA into anintelligent automationecosystem. In this model, RPA handles execution and integration, while AI provides understanding and decision-making.
Example 1: Intelligent Document Processing
Consider a high-volume document workflow, such as processing incoming invoices or claims.
- AI reads and interprets documents, extracting fields like vendor name, amounts, or claim details.
- RPA enters the extracted datainto ERP, CRM, or claims systems, updates status, and triggers approvals.
The result is a largely touchless process, faster cycle times, and more consistent compliance.
Example 2: AI-Powered Customer Support Automation
In a support center, you can combine both technologies:
- AI classifies incoming emails or chat messagesby topic, urgency, or sentiment.
- RPA creates or updates tickets, retrieves account data, and triggers follow-up workflows.
This combination reduces manual triage, speeds up responses, and ensures that agents have the right context immediately.
Example 3: Predictive Operations and Automated Actions
In operations, you can turn predictions directly into action:
- AI predicts equipment failuresbased on sensor and historical data.
- RPA triggers maintenance workflows, schedules technicians, and updates asset management systems.
Teams move from reacting to problems to preventing them, improving uptime and customer satisfaction.
Strategic Considerations for Leaders
To get the most from AI and RPA, it helps to think in terms of a broader automation strategy rather than isolated projects.
1. Start with Processes, Not Just Technology
Map your most important workflows and identify where time, cost, or quality issues are highest. Then decide where RPA, AI, or a combination will have the biggest impact.
2. Design for People + Machines
The most successful automation programs are built aroundhuman-machine collaboration. Aim to:
- Offload repetitive tasks to bots.
- Use AI insights to support, not replace, expert judgment.
- Give employees visibility into what bots and models are doing.
3. Build Reusable Components
RPA workflows and AI models can be reused across departments. For example, an AI model that classifies documents for finance may also support legal or procurement with minimal changes.
Choosing Your First (or Next) Project
Whether you are just starting or expanding your automation footprint, picking the right use case is critical for momentum.
High-Value RPA Candidates
- High-volume, repetitive tasks with clear rules.
- Processes that span multiple systems and require manual integration.
- Tasks with measurable error rates and rework costs.
High-Value AI Candidates
- Areas with abundant historical data that is currently underused.
- Decisions that rely on pattern recognition or complex trade-offs.
- Customer journeys where personalization could drive higher engagement or revenue.
AI vs RPA: Key Takeaways
- RPA automates how work is done, following rules to perform tasks quickly and accurately.
- AI enhances how decisions are made, learning from data to interpret, predict, and recommend.
- Together, they form intelligent automation—linking smart decisions with reliable execution.
- You do not need to choose one over the other; your best strategy is often a balanced mix tailored to your processes and goals.
By understanding the strengths ofartificial intelligence vs RPAand how they complement each other, you can design an automation roadmap that boosts efficiency today while building intelligent capabilities for tomorrow.
